Table Of Content
- It cannot be used to analyze behavior over a period of time
- Participants
- Considerations for use: Prevalence Odds Ratio versus Prevalence Ratio
- Limitations of Cross-sectional studies
- Characteristics of cross-sectional studies
- Cross-sectional study examples
- What are the limitations of cross-sectional studies?
While this study cannot prove that overeating causes obesity, it can draw attention to a relationship that might be worth investigating. Cross-sectional studies are also unique because researchers are able to look at numerous characteristics at once. Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education.
It cannot be used to analyze behavior over a period of time
Although researchers get to analyze these variables, they do not manipulate them. The participants in this type of study are selected based on particular variables of interest. Cross-sectional studies are often used in developmental psychology, but this method is also used in many other areas, including social science and education. As discussed in the earlier articles, we have highlighted that in an observational study, the investigator does not alter the exposure status. The investigator measures the outcome and the exposure(s) in the population, and may study their association.
What Is a Longitudinal Study? - Verywell Mind
What Is a Longitudinal Study?.
Posted: Sat, 02 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Participants
If learners are not immersed in the simulation, their ability to achieve learning outcomes is not only affected but can also lead to anxiety, which can hamper their collaboration with their peers [11]. This suggests that a simulation design that increases physical, conceptual, and psychological fidelity is necessary to induce flow, as flow increases students’ motivation, enjoyment, and satisfaction with the learning process. The design’s inherent nature makes it inexpensive to conduct and can yield multiple independent (predictor) and dependent (outcome) variables (Cummings, 2013).
Considerations for use: Prevalence Odds Ratio versus Prevalence Ratio
A researcher might collect cross-sectional data on past smoking habits and current diagnoses of lung cancer, for example. While this type of study cannot demonstrate cause and effect, it can provide a quick look at correlations that may exist at a particular point. However, these datasets are often aggregated to a regional level, which may prevent the investigation of certain research questions. You will also be restricted to whichever variables the original researchers decided to study. Sometimes a cross-sectional study is the best choice for practical reasons – for instance, if you only have the time or money to collect cross-sectional data, or if the only data you can find to answer your research question were gathered at a single point in time.
These sponsors had no role in the study design; in the collection, analysis or interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the article for publication. The confidence level (1-α) was 0.95; the proportion of main outcome (depression and anxiety) was 0.1; The confidence interval width (two sided) was 0.03. The confidence interval formula was Exact (Clopper-Pearson); the 2-tailed P value was 0.05. It was calculated by PASS 11.0 (Power Analysis and Sample Size 11.0, NCSS Inc., USA) [8, 10, 18].
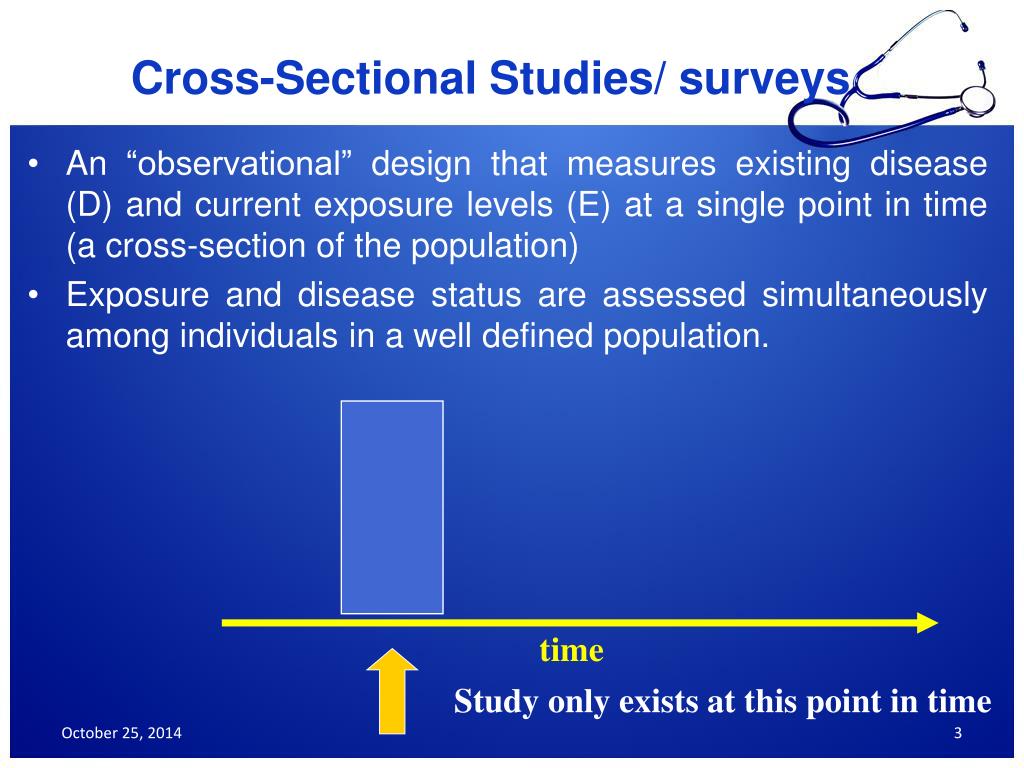
Characteristics of cross-sectional studies
We can measure the prevalence of disease or calculate the OR as a measure of association. However, due to the nature of study design, in general, it is difficult to derive causal relationships from cross-sectional analysis. First, due to the cross-sectional nature of the study, we could not establish a causal relationship between the choice of smoke-free policies and sociodemographic and smoking-related variables. Second, we used self-reported data that are subject to recall and social desirability bias.50 51 These two types of bias may result in underestimation or overestimation of the association between the outcome variable and other variables.
Information was gathered through a questionnaire that individuals completed themselves. The mental health of the participants was assessed using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Assessment-7. Binary logistic regression was used to calculate adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals. 4) The mediating effect of flow on the relationship between simulation design and simulation educational satisfaction was examined using simple and multiple regression analyses based on the methodology of Baron and Kenny’s three-step procedure. This highlights the value of the flow experience in enhancing intrinsic motivation in remote learning, which depends on learners’ self-direction, and in producing excellent learning outcomes [19].
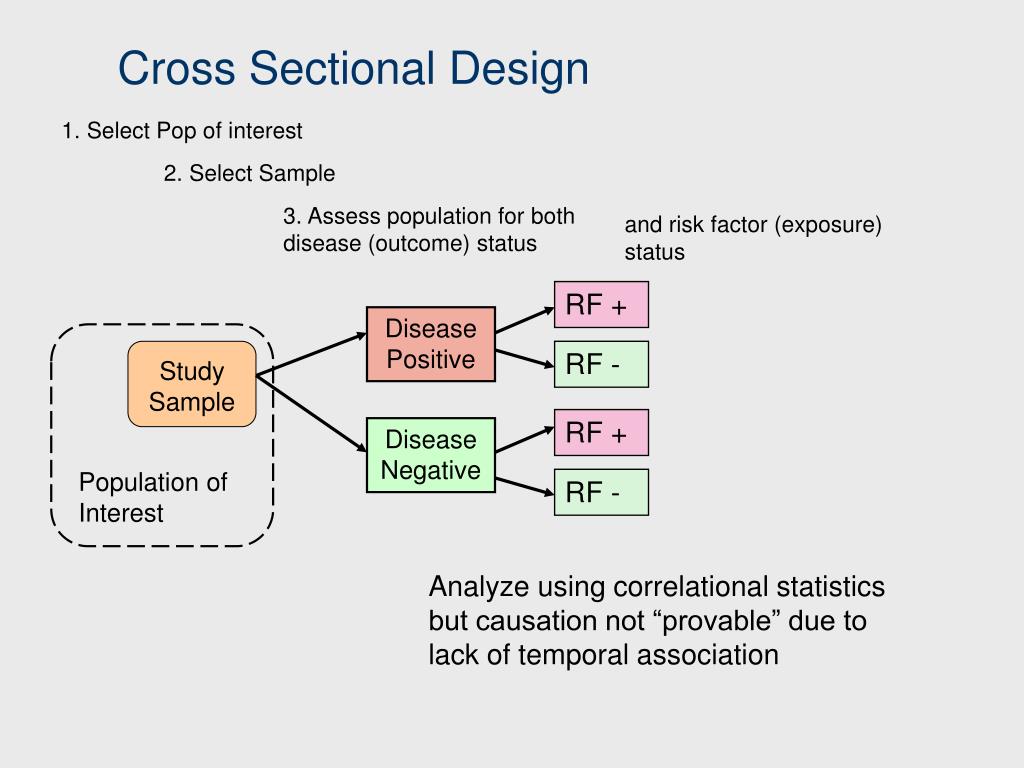
Cross-sectional studies can be useful research tools in many areas of health research. By learning about what is going on in a specific population, researchers can improve their understanding of relationships among certain variables and develop additional studies that explore these conditions in greater depth. For example, researchers might be interested in learning how exercise influences cognitive health as people age. They might collect data from different age groups on how much exercise they get and how well they perform on cognitive tests. Conducting such a study can give researchers clues about the types of exercise that might be most beneficial to the elderly and inspire further experimental research on the subject.
Student feelings assume a fundamental part in comprehension that relates to the securing and moving of information and clinical abilities [28]. This cross-sectional study was conducted using 143 fourth-year nursing students who had participated in classes using simulations at three universities in Seoul, Daegu, and Jeonbuk. Demographic data, simulation design scale (SDS), flow in simulation, and the educational satisfaction scale in simulation were collected via an online questionnaire. The collected data were analyzed through t-test, ANOVA, Scheffé test, and Pearson’s correlation coefficient using SPSS 25.0. The mediating effect of flow was analyzed through the three-stage mediation effect procedure using hierarchical regression analysis and the Sobel test.
Longitudinal studies and cross-sectional studies are two different types of research design. In a cross-sectional study you collect data from a population at a specific point in time; in a longitudinal study you repeatedly collect data from the same sample over an extended period of time. A cohort study is a type of longitudinal study that samples a group of people with a common characteristic. One key difference is that cross-sectional studies measure a specific moment in time, whereas cohort studies follow individuals over extended periods. Findings from this study showed that residents whose family members smoked were more supportive of smoke-free building policies than those whose family members did not smoke.
Participants in longitudinal studies have to commit for an extended period, which significantly increases costs. Cross-sectional studies are at risk of participation bias, or low response rates from participants. If a large number of surveys are sent out and only a quarter are completed and returned then this becomes an issue as those who responded may not be a true representation of the overall population. Please note the Introduction, where there is a table under "Which study type will answer my clinical question?". You may find that there are only one or two question types that your study answers – that’s ok. Cross-sectional studies are not the best choice for studying rare events because of the need for a sufficiently large sample size to obtain meaningful results.
This study showed a positive association between BMI and poor mental health (anxiety and depression) among Chinese nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in those who were overweight or obesity. Participants with elevated BMI, impaired sleep quality, and diminished scores in perceived organizational support, efficacy, hope, resiliency, and optimism exhibited an increased likelihood of developing depression, as indicated by the univariate analysis. A greater proportion of individuals with depression exhibited concurrent alcohol consumption, had siblings, encountered significant life events, had infrequent social interactions with friends, had employment tenure exceeding five years, and worked in excess of 40 h per week. The factors stated above exhibited statistical significance in the univariate analysis, as shown in detail in Table 1. The present cross-sectional investigation was carried out at a Chinese hospital throughout the period from March 2022 to April 2022.
No comments:
Post a Comment